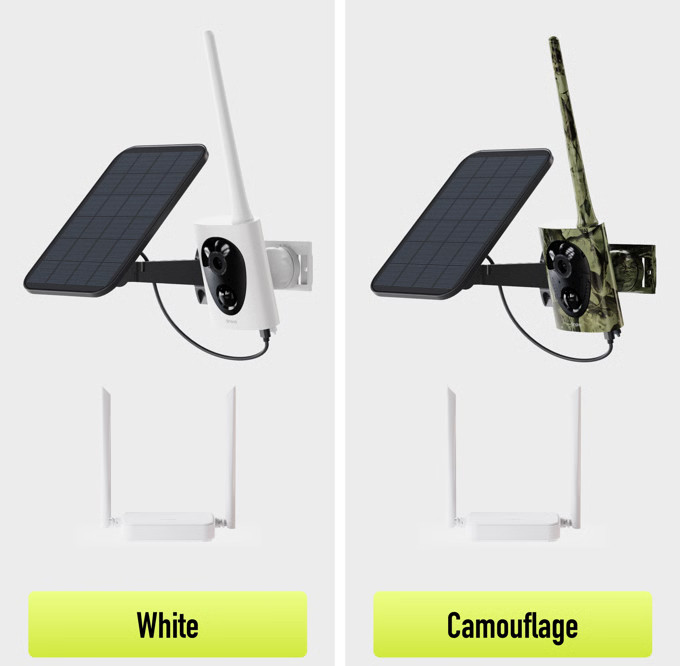

If you haven’t seen the ads, here’s a link to the new Kickstarter for the “1-Mile WiFi Camera.”
TL;DR: this is a really cool idea, and I like it. However, these cameras won’t work with “normal” WiFi like AyrMesh; they use a special form of WiFi called “WiFi HaLow” (802.11ah), which requires a separate access point. They also sell an access point, but it’s an indoor-only unit that cannot be mounted outdoors, and I’m not entirely sure the effective range of the cameras will be longer than a good WiFi camera with an external antenna and one or more AyrMesh Hubs. I think they’re significantly over-stating the capabilities of the system – it might reach a mile under optimal conditions, but probably not in most conditions. All that said, I still think it’s really cool, and I’ll be excited to hear from folks who use it.
Long-Winded Explanation
I was really excited to see this, because I have been trying to get camera vendors to build long-distance WiFi cameras: battery-operated cameras with solar panels and large, external antennas to extend the range of the cameras to the WiFi access point (like an AyrMesh Hub). The only ones I know of are the Reolink Argus Eco line of cameras. Although they come with relatively small, low-gain antennas, some of the models have RP-SMA antenna connectors that can accept a higher-gain antenna (which you’d have to buy separately – something like this or even this) to maximize their range.
The “1-mile WiFi Camera” does use batteries, a solar panel, and a nice, big, external antenna, which was exciting for me to see. However, closer inspection reveals that it uses WiFi, but only a special and seldom-used form of WiFi called “WiFi HaLow.” This special kind of WiFi has been around for several years, but it is seldom used because it operated on the 900 MHz. band, so very few devices are equipped to connect to it.
Using 900 MHz. is a good idea – it has historically been significantly less congested than the “normal” 2.4 GHz. (2400 MHz.) WiFi band. Because it uses a significantly lower frequency, it is also significantly less affected by obstructions like trees, bushes, and even non-metallic walls. Make no mistake: it’s still at the low end of the “microwave” spectrum, so the signal is still weakened by those obstructions, but not as much as 2.4 GHz. WiFi (and much, much less than 5.8 GHz. or 6 GHz. WiFi, which are not that useful for outdoor WiFi).
I had hoped that 802.11ah might be included in the 802.11ax specification, also known as “WiFi 6,” but it wasn’t. I then hoped it might be included in the 802.11be specification, known as “WiFi 7,” but that didn’t happen, either, so 802.11ah “WiFi HaLow” remains a separate and distinct form of WiFi with very few supported devices.
Because of this, the folks behind the “1-Mile Camera” also sell a WiFi HaLow access point to provide the signal for the camera’s use. This access point is just like the AyrMesh Gateway Hub – it needs to be connected to your router and positioned as high as possible for maximum range. However, it is an indoor device, so you want to get it up on an upper floor or in the attic for maximum range. It’s disappointing that they don’t offer an outdoor access point, because, like the AyrMesh Hubs, that would be more effective.
I should mention that outdoor HaLow access points do exist; Rokland carries an Alfa access point that should work well with these cameras.
One other little fly in the ointment is that, while I mentioned earlier that the 900 MHz. band has historically been less congested, that is changing quickly with the widespread use of LoRa. LoRaWAN has become popular for long-distance, low-bandwidth connections using the same 900 MHz. band, and new “modes” for LoRa like Meshcore and Meshtastic are increasingly popular. All of these add noise to the 900 MHz. band, making it harder for the wide-banded HaLow to work well. The 900 MHz. band is only 26 MHz. wide, and HaLow channels are 16 MHz. wide, so there isn’t even room for two non-overlapping channels. However, HaLow can use OFDM, meaning it divides that 16 MHz. channel into 1-MHz. wide sub-channels, so it can be pretty nimble about “stepping around” interference. However, having to ignore some of those sub-channels reduces the bandwidth (speed) of the HaLow connection, and bandwidth matters much more for cameras.
Conclusion: Maybe Over-Hyped, but Still Interesting
So, to be clear, I think the “1-Mile Camera” claims are a bit overblown. I do think you could use a camera a mile away in perfect conditions: the access point in a high window in a multi-story building, looking out over a very flat area with no (or very few) obstructions and very little interference, and the camera also mounted quite high in the air. In normal operation, I’d expect quite a bit less… BUT I still think that’s pretty cool! I’m eager to hear how “real people” (not paid endorsers) find it.
My counter to the “1-mile camera” is pretty simple: meshing WiFi like AyrMesh can be used to extend regular WiFi (the kind “normal” WiFi cameras, your phone, your tablet, and your laptop use) out a mile, or 2, or 5, or more. This provides a lot more flexibility, because a lot more devices can use the network. It requires more setup than the “1-Mile Camera” promises, but I think any real, working solution will require a fair bit of work to extend a signal a long distance with good bandwidth. As much as I want to see HaLow succeed (and I really do!), I think that the 2.4 GHz. AyrMesh solution is much more practical for the forseeable future.
We’ll be interested in hearing what you think about this.

 There is an image of farming – bucolic, peaceful, unfettered by the concerns of the technological age. It’s lovely, and many of us indulge it to some degree… but it is patently false. Agriculture is an industry moving quickly on the technology curve as markets demand more, higher-quality, and cheaper food and grains. Specialized implements, higher-horsepower machines, GPS steering, variable rate planting and spraying, and the cellphone have all had an impact on farm productivity. But that’s not all.
There is an image of farming – bucolic, peaceful, unfettered by the concerns of the technological age. It’s lovely, and many of us indulge it to some degree… but it is patently false. Agriculture is an industry moving quickly on the technology curve as markets demand more, higher-quality, and cheaper food and grains. Specialized implements, higher-horsepower machines, GPS steering, variable rate planting and spraying, and the cellphone have all had an impact on farm productivity. But that’s not all.


 The new AyrMesh Hub2x2
The new AyrMesh Hub2x2


 We are pleased to introduce the new model of the
We are pleased to introduce the new model of the  The ability to mount the Receiver on a flat surface (without additional hardware) is a feature that many users requested over the years, and the ability to add an outdoor PoE device will, we think, enable our customers to enhance security and operational awareness.
The ability to mount the Receiver on a flat surface (without additional hardware) is a feature that many users requested over the years, and the ability to add an outdoor PoE device will, we think, enable our customers to enhance security and operational awareness. The other interesting change is the addition of a “gland” on the bottom of the radio. This gland makes it a bit trickier to install the Hub, but it protects it from water splashing up from below. This addresses concerns we have heard from some livestock operators who want to put Hubs near livestock pens or in milking parlors or farrowing houses, but worry about having to spray water around the Hub. We still don’t recommend spraying water directly up at the Hub, but this Hub will better withstand inadvertent sprays of water from below.
The other interesting change is the addition of a “gland” on the bottom of the radio. This gland makes it a bit trickier to install the Hub, but it protects it from water splashing up from below. This addresses concerns we have heard from some livestock operators who want to put Hubs near livestock pens or in milking parlors or farrowing houses, but worry about having to spray water around the Hub. We still don’t recommend spraying water directly up at the Hub, but this Hub will better withstand inadvertent sprays of water from below. I have a Google Alert for “Wireless Farm” – I get about an article a week (and many of them are about wireless technologies for “server farms” and other odd things). But today I got a link to this article about “
I have a Google Alert for “Wireless Farm” – I get about an article a week (and many of them are about wireless technologies for “server farms” and other odd things). But today I got a link to this article about “

 Since we started marketing the AyrMesh system five years ago, we have gotten inquiries from folks who have large houses, offices, and small hotels/motels – can AyrMesh work indoors? The answer, of course, is that it can work, but it’s not optimal for a number of reasons, and we do not recommend it. AyrMesh is designed for outdoor use, mainly in rural areas.
Since we started marketing the AyrMesh system five years ago, we have gotten inquiries from folks who have large houses, offices, and small hotels/motels – can AyrMesh work indoors? The answer, of course, is that it can work, but it’s not optimal for a number of reasons, and we do not recommend it. AyrMesh is designed for outdoor use, mainly in rural areas. Open-Mesh uses their
Open-Mesh uses their